A groundbreaking study has uncovered vast reserves of natural hydrogen deep within Earth’s continental crust, potentially providing a clean energy source capable of powering humanity for the next 170,000 years.
Researchers from the University of Oxford, Durham University, and the University of Toronto have discovered that this naturally occurring hydrogen, often referred to as “white hydrogen,” could serve as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Unlike conventional hydrogen production methods that emit carbon dioxide, white hydrogen is formed through natural geological processes and can be extracted with minimal environmental impact.
The study highlights the significance of this discovery in the context of global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and transition to cleaner energy sources. The researchers emphasize that tapping into these natural hydrogen reserves could revolutionize energy systems worldwide, providing a long-term solution to the ongoing energy crisis.
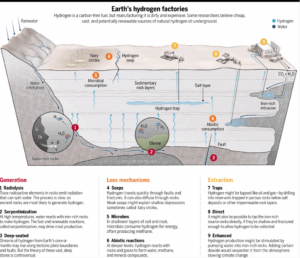
However, the extraction and commercial viability of natural hydrogen present challenges. The researchers note that while the reserves are substantial, developing efficient and cost-effective methods for extraction is crucial. Additionally, further research is needed to understand the distribution and replenishment rates of these hydrogen deposits to ensure a sustainable supply.
This discovery marks a significant milestone in the search for clean energy alternatives and underscores the importance of continued research and innovation in the field of renewable energy. As the world seeks to mitigate the impacts of climate change, harnessing natural hydrogen could play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable energy future.


